VBA is year a leap year
0. Quick guide - test for leap year
In this module:
- Leap year function - from first principles
- Leap year function - using VBA functions: DateSerial, Month, and Year
1. Leap year
A leap year is:
- Any year that is exactly divisible by 4 ✅
- except if exactly divisible by 100 ❌
- but if exactly divisible by 400 ✅
- except if exactly divisible by 100 ❌
The extra day is added to the month of February, with 29th February often described as a leap day. Exactly divisible means remainder 0 and can be determined by the VBA Mod operator.
The leap year calendar adjustment is needed because the earth rotates at 365.242375 times per year.
- Point 1 adds \(+0.25\)
- Then is corrected every 100 years in point 2 giving \(-0.01\)
- Finally point 3 adds 1 days every 400 year, equivalent to \(+0.0025\).
- The result: \(365 + 0.25 - 0.01 + 0.0025 = 365.2425\).
2. VBA code leap year identification
2.1 Using logic components
Code 1 and 2 are variations of the logic depicted in part 1 points 1 to 3. The VBA Mod operator divides two numbers and returns only the remainder.
Code 1: Function
xlfIsLeapYear_v1 returns the Boolean value TRUE if Year is a leap year
Function xlfIsLeapYear_v1(Year As Integer) As Boolean
Dim bLY As Boolean
' -- point 1 --- --- point 2 ---- --- point 3 ----
If Year Mod 4 = 0 And (Year Mod 100 <> 0 Or Year Mod 400 = 0) Then bLY = True Else bLY = False
xlfIsLeapYear_v1 = bLY
End Function
Code 2 uses an If...Then construct to achieve the same outcome.
Code 2: Function
xlfIsLeapYear_v2 returns the Boolean value TRUE if Year is a leap year.
Function xlfIsLeapYear_v11(Year As Integer) As Boolean
Dim Tmp As Boolean
If Year Mod 400 = 0 Then ' point 3
Tmp = True
ElseIf Year Mod 100 = 0 Then ' point 2
Tmp = False
ElseIf Year Mod 4 = 0 Then ' point 1
Tmp = True
Else
Tmp = False
End If
xlfIsLeapYear_v2 = Tmp
End Function
VBA dates run from 1 January 100 to 31 December 9999 with corresponding serial date values -657434 to 2958465
Excel dates run from 1 January 1900 to 31 December 9999 with corresponding serial date values 1 to 2958465. Negative serial dates are not recognised in Excel. It is well known that the serial date sequence is incorrect because Excel includes 1900 as a leap. Thus 29th February 1900 with serial date value 60 is an error (inherited from Lotus 123). The VBA based functions in code 1, 2 and 3 each handle the 1900 date error correctly.
Table 1: A comparison of WS and VBA dates
| Date | Excel WS | VBA |
|---|---|---|
| 1 January 100 | ######## | -657434 |
| 30 December 1899 | ######## | 0, stored as 12:00:00 AM |
| 31 December 1899 | ######## | 1 |
| 0 January 1900, WS date format applied to zero | 0 | |
| 1 January 1900 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 January 1900 | 2 | 3 |
| 28 February 1900 | 59 | 60 |
| 29 February 1900 (the 1900 leap year error) | 60 | 61, stored as 1 March 1900 |
| 1 March 1900 | 61 | 61 |
| 31 December 2030 | 47848 | 47848 |
2.2 Using the VBA date functions
This is another variation uses VBA functions DateSerial, Month, and Year.
Code 3: Function
xlfIsLeapYear_v3 returns the Boolean value TRUE if Year is a leap year
Function xlfIsLeapYear_v3(Year As Integer) As Boolean
xlfIsLeapYear_v3 = Month(DateSerial(Year, 2, 29)) = 2
End Function
Note: the WS version of code 3 would fail in the year 1900. See lines 2 and 3 of the worksheet in figure 1.
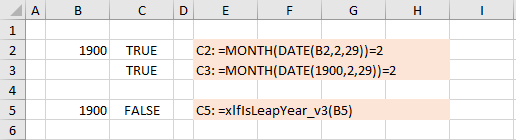
WS formula line 3 =MONTH(DATE(1900,2,29))=2 returns TRUE ❌
WS formula called from VBA Application.ExecuteExcel4Macro("MONTH(DATE(1900,2,29))=2") returns FALSE
- Development platform: Office 365 ProPlus Excel 64 bit.
- Published: 29th February 2016
- Revised: Friday 24th of February 2023 - 03:12 PM, Pacific Time (PT)